|
 |
|||||||||||

A
lake can be sectioned into large portions known as "lake
zones". These zones are not easily defined and indeed are
very generalized in comparison to geographic features such as
break lines, channels and flats. 1-
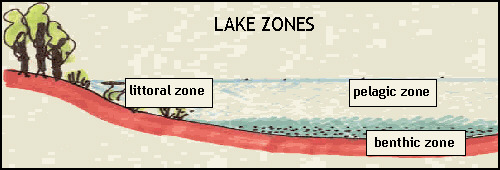
Littoral Zone. The lakes littoral zone is the area around
the lake edges where sunlight penetrates to a depth where aquatic
plant life (water weed and phytoplankton) are no longer present.
The aquatic weed and phytoplankton are the basis of the aquatic
foodchain which supports the most diverse life forms ranging from
aquatic plant life, zeoplankton, crustacean and fish. 2- Pelagic Zone. The centre of a large lake basin is not dissimilar to the middle of an ocean. Water depths are great and there is no significant structure near the water surface. Aquatic life is adapted to suspending or floating on or near the surface of the lake. Small plankton build up significant numbers to create the base of another foodchain with ultimately larger fish species at the top. 3- Benthic Zone. Only a few organisms are capable of premanent residency in this zone. Due to lack of oxygen and light at these depths the aquatic weed and fish life are non existent. There are some organisms that assist in the decomposition of dead matter that finds its way down to these dark depths. Water
Level Fluctuations South
East Queensland has seasonal weather patterns that are generally
predicatable such as wet and dry seasons, as in many other parts
of Australia. Impoundments were built as important water storage
facilites for rural or domestic use. As consumers, we have regular
patterns of water consumption, water levels are controlled or
manipulated by the water board who monitor and distibute the resource
accordingly. A dams water level will rise and fall periodically
over a season and in some instances it may remain static for several
months or years.
|